Baking Tips
You are here: Home > Useful TIPS (Kitchen and Cooking) > Baking Tips
Baking is an art. Baking is fun. Baking is about precision, timing, and knowing your basics so that all your effort pays off in the end. Here are some tips and techniques that all home bakers should know.
This post will be updated regularly with facts as I am able to add them.
WHAT KIND OF OVEN ?
First and foremost, know your oven! Different kinds of ovens, work slightly differently. So you need to know what kind of oven you are using to begin with. You will always see recipes stating the fact that oven temperatures vary so I suggest you make a note the next time you bake a perfect cake something similar if you used the exact temperature as stated in the recipe you followed. However, if you did so and the cake was overcooked or undercooked, you might try the same recipe again with the temperature increased or decreased by 10 °c / 50° F. (It helps if you are using a basic, reliable cake recipe for this).
Types of Ovens:
An oven consists of an insulated cavity in which food is heated and cooked. The temperature can be controlled and maintained during the cooking process. That means the heating element will fluctuate to maintain the temperature that you have set.
Sometimes, the food is cooked from below (as in traditional Baking or Roasting). And sometimes, the food is cooked from above (as in Broiling).
Some ovens have neat labels, that say bake, broil, roast, etc. Other European models, show you the direction of the heating element. Heating element, from below and above, heating element from below only or heating element from above only. You should always remember to set this correctly before you begin. Some ovens even have a heat source from the back.
Now, we address the issue of those ovens, where you can adjust the direction of the heat source. Traditionally, for baking, only the bottom heat element is used. However, for some ovens, you might get better results if you use both top and bottom elements. This is the same in the case of Roasting. For broiling, usually, you switch to the top heat element after having roasted from the bottom first for a period of time. You can also place the item to be broiled closer to the top of the oven while doing this. If you are using the Rotisserie function, it is best to have all heat elements switched on.
Conventional Oven VS Convection Oven:
In a Conventional oven, the heat source is stationary, usually radiating heat from the bottom. These are the ovens that are most commonly, found in regular home baking.
In Conventional ovens, there are what is known as heat pockets, there are areas of the oven that are hotter, and you must identify these hot pockets to suit your cooking.
In a Convection oven, there is a fan usually on the back of the oven, to regulate the heat more consistently, providing faster baking.
The fans in the Convection oven, on the other hand, circulate the heat in the oven in such a way that heat is evenly distributed throughout the cooking process and the food is cooked quicker. If you are using a convection oven, you need to reduce your temperature SLIGHTLY from the temperature stated in regular recipes.
Baking Tips – Following Recipes For Baking:
Always retain the instruction manual and recipe guides you get one with your oven, they give you the best temperatures and procedures. Use this as a guideline when following other recipes.
Whenever you follow a recipe, always use your discretion. Remember that you know your oven best. Do not follow timings and baking temperatures blindly. Keep checking on the cake or food in the oven, you can always stop the cooking process if you feel it is done even before the specified time. Likewise, you may need to bake for more than the specified time. If you feel a cake is browning too fast on the top and still uncooked on the bottom, you can cover it with tin foil for the remainder of the cooking time.
The more you use your oven the more you will get to know when a cake or baked good is done to perfection.
Learn to use all your senses. Smell it : you can tell when the cake is baked perfect once you get the hang of it. Listen to it: Hissing noises from the oven often tell you about how done a bread is. Have a Look: You can see how a cake domes, if it leaving the sides of the pan, if cheese is melted etc..
What do these symbols on my oven MEAN?
Depending on what type of oven you are using, here are a few symbols and what they mean.


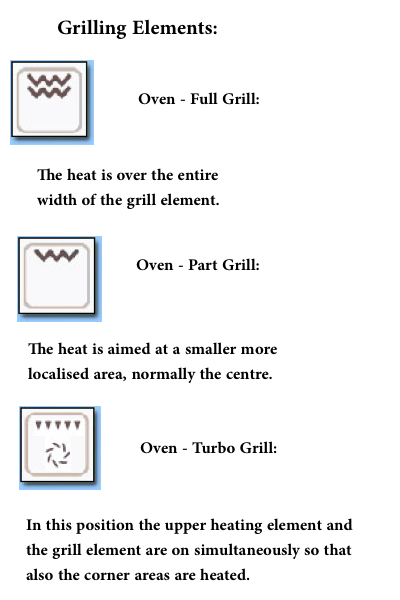
Bakeware
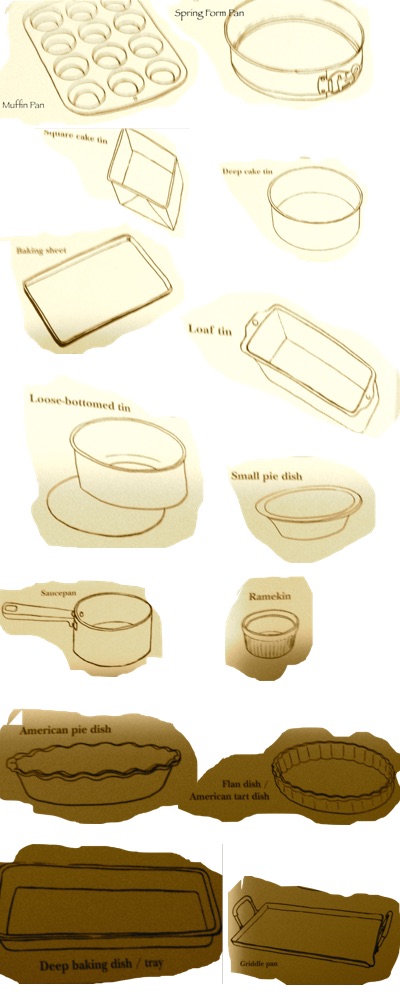
Choosing the correct bakeware for the dish you need is essential. Bakeware can be made of glass, aluminum, cast iron, nonstick Teflon or ceramic. Having a wide range of bakeware in different sizes is great for a well-rounded baker.

METAL Bakeware: is often offered in aluminum, glazed aluminum, anodized aluminum, and different nonstick coated metals. I really like commercial aluminum baking pans. They look simple but provide great results. They are also very durable.
Anodized Bakeware has a darker finish, with slight nonstick properties although not complete. The darker color can cause faster browning.
Non-Stick Bakeware allows for the easiest release but being dark in color, it also causes faster browning and hardening of crust.
Glass Bakeware (Pyrex) is great for seeing how a cake is rising or seeing if the bottom is cooked. but you usually need to reduce the temperature slightly if using glass. And once baked make sure the product does not “sweat” inside the glass dish. This will cause the woods to become stale quicker.
Other Accessories you will need:
Measuring cups: metal, plastic, and glass. so with pouring spouts and some with round edges. Measuring spoons. Good to have a set that measures approximates in grams too, besides the usual Tbsp, tsp etc.
Rolling pins: Wooden, Acrylic, and Metal are used. A ‘Tapered Pin’ is one without handles and is good for pie pastry, cut cookies, etc. Use larger pins for yeasted doughs.
Whisks: in many different shapes and sizes are available. You can use it to mix both dry and wet ingredients, to whisk ad to melt chocolates, etc…
Dough Scrapers or Bench Cutters: to divide and cut portions of dough is very handy.
Fruit zester and mini graters are great to have in your kitchen for that additional tiny bit of this and that.
Parchment Paper: Baking Paper is used to line trays and can prevent scorched bottoms on cookies and the like. It is different from wax paper which smokes up if used to line pans in the oven.
Baking mats: are used like parchment paper to line baking trays but are expensive. They have great nonstick quality and easily washable.
Baking Stone: A baking stone is great to keep on the lower rack of your oven. If preheated in the oven it gives you fast even heat throughout the oven.
Spatulas and Wooden Spoons: Large and small-sized offset and flat spatulas come in handy when decorating cakes. Wooden spoons in sorts of sizes are a must-have to mix different kinds of ingredients seperately.
Wire racks: Metal wire racks help to cool off baked cakes cookies etc.. Wire racks are also used to grill kebabs to help the oil drip to the tray below.
Pastry brushes: are useful to apply egg wash or spread sugar glaze on baked goods, before and after baking. Also god for oiling pans.
Avid bakers list: cupcake and Muffin Liners, Cardboard cake plates/boards covered in foil – in different sizes, foldable cake boxes, cake stands, plastic cake boxes, turntables, cake stands, cake covers, piping nozzles collections, etc…
Appliances: Stand Mixers, Hand Mixers, Food Processors, Cream chargers, Bread Machines, Ovens
Common Ingredients in Baking:
Flour:
All-Purpose Flour: Or Unbleached All-purpose flour. If a recipe states an ingredient as just flour, or plain flour – it’s referring to All-Purpose Flour. ‘Unbleached’ refers to the fact that it has naturally aged and lightened in color as it has matured without any chemical process to whiten it.
Bread Flour or Unbleached Bread Flour: is flour that is designed for yeasted baking. It has a stipulated percentage of protein which helps to create more gluten and more rise in baked bread.
Whole Wheat Flour comes in stone-ground, regular or white varieties. Stone-ground wheat flour contains all the components of the wheat berry, hence more nutritious. Regular Whole Wheat Flour is basically flour that has been stripped of nutrients to make plain white flour and then some of the bran is re-added. It is lacking in nutritional value. Wheat Flour that is Labeled WHITE Whole Wheat Flour, is nutrient-dense. It is great when baking cookies, muffins, or scones, and you want more nutritional value.
Cake Flour: this is different from All-Purpose Flour. It gives a finer texture to cakes due to being more finely ground. In some countries Cake Flour is chlorinated.
Self Raisin Flour:is Flour mixed with Leaveners. This can help eliminate the problem of unevenly distributed leavening agents.
Spelt, Multigrain, Rye(Pumpernickel), Kamut, Cornmeal, Graham Flour: These are nutritional flours that are specific to certain types of baking. They can most often be seen in the ORGANIC Sections. Make sure to look for Stone Ground Varieties.
Sweeteners:
Sugar:
White sugar or Granulated Sugar is what most recipes call for. It can be fine or coarse-grained. To make super fine-grained sugar, simply pulse it a few times in a food processor without turning to a powder. It is best to measure sugar using round-edged scooping cups and not spouted measuring cups because they do not always measure the same.
Brown Sugar comes dark or light and contains molasses. The darker, the denser. When measuring brown sugars, it is best to use round scooping cups and level – off by patting down. This is called ‘ Firmly Packed’.
Confectioners Sugar: Also known as Icing sugar or powder sugar, is white sugar that has been finely pulverized along with cornflour/cornstarch. It is used in butter-based Icings, whipped cream, fondant, or for sprinkling.
Honey: Honey helps give baked goods the loveliest golden color. Be careful not to bake at high temperatures though as the gold can turn burnt quite quickly. Honey also offers a lovely floral fragrance. Tip: to measure honey spray your scoop/cup/spoon with vegetable oil before measuring. This helps to release the honey easily.
Fats:
Butter: Most recipes that call for butter are asking for Unsalted Butter. This is the best butter for baking. Salted butter should only be used if specified.
Oils: Vegetable, Canola, Sunflower, Olive, etc… You can replace some recipes with vegetable oil or the likes unless mentioned otherwise. Oil helps to keep baked goods for longer. Flavor-wise there is no enhancement, however, in some cases, it makes the cake super moist. Oils can make replacements for butter in cakes, muffins, and loaves but are not recommended in biscuits, cookies, scones or pie pastry.
Margarine: is often used for dietary reasons and in certain recipes. Margarine usually contains some amount of salt. It is yellowish in color. Look for the less salty ones. Margarine does not measure the same as butter due to the water and air that it is inflated with.
Shortening: Is made from hydrogenated vegetable oil and is white or light in color. It is good for pie pastries or doughnuts. Look for the ones without Trans Fats.
Eggs: Eggs add flavor, and color and provide leavening in recipes. It is recommended to use large-sized eggs as opposed to extra-large or medium in most cases. Also note that the more eggs in a recipe, the more size will have a significant impact. Eggs for baking should be brought down to room temperature. This helps them gain maximum volume while whipping. It is okay to use both brown, white, or omg 3 enriched eggs.
Eggs add flavor, and color and provide leavening in recipes. It is recommended to use large-sized eggs as opposed to extra-large or medium in most cases. Also note that the more eggs in a recipe, the more size will have a significant impact. Eggs for baking should be brought down to room temperature. This helps them gain maximum volume while whipping. It is okay to use both brown, white, or omg 3 enriched eggs.
Milk: Milk helps to tenderize and enhances browning in baked goods. It also enhances and expands the crumb ( the internal structure of the cake etc). The fat content in milk does not make much of a difference. Milk should be at room temperature for baking.
Creams:

The type of cream will always be specified in a recipe and they all work differently due to the fat over milk ratio. Heavy, Light, Whipping.., etc. Sometimes Evaporated Milk can be used in place of Light Cream. If a recipe calls for whipping cream, there is usually no good substitute. Creams come in the cold section ad also in (Long life) canned and carton packing, depending on the type.
Buttermilk, Yoghurt, Sour Cream, Sour Milk, Buttermilk Powder: These milk products provide lovely results in baking. I especially love buttermilk. Biscuits, Cakes, Pancakes. The acid in these souring agents, work happy with the baking soda in the recipe to produce add ‘lightness’. Nowadays buttermilk comes in powdered form and can be blended with dry ingredients. Sour cream is like a thicker creamier yogurt. All these milk products have similar effects and sometimes can be used in place of one another. They all add a little characteristic tang and help muffins, cakes, and quick breads to rise.
Leaveners: (Rising Agents) – There are physical factors that help baked goods to rise such as steam and air and there are also chemical agents like baking soda and baking powder, yeast, and eggs. Sometimes you only need one leavened. Sometimes you need a combination.
Yeast: there are various types of yeast available. fresh and dry. Read the label to see when the yeast is to be added. When you add yeast to lukewarm water along with sugar, it should become frothy and sell yeasty and make some bubbles after about 10 minutes. This is called proofing. If there is no activity at all, it is quite possible your yeast has grown old and is best not used in the recipe. This process helps you save valuable ingredients from going to waste. Remember that yeast needs warm water that is not too hot or it will kill the yeast. Dried yeast that comes in packets must be refrigerated once opened. make sure to fold and seal the packets up to the yeast level as moisture and air can cause the yeast to age quickly. Once opened this yeast should be used within 4 months. When using yeast from the fridge, it must be left out at to come to room temperature before using. Rapid Rise yeast can be added directly to flour according to package directions. Never mix yeast directly with icy/ cold ingredients.
Baking Soda: Baking Soda is comprised of soda and is used in recipes where there is more acid involved, from buttermilk, etc… There are also some cookies and breads that rely only on baking soda as well. Baking Soda keeps for a long time. However, it can absorb smells from different foods. If your baked goods taste unusually soapy or “off” you probably added too much baking soda.
Flavoring:
Salt: Salt is essential not only in savory dishes but also in sweet baked goods. It is an essential balancing agent. In yeast doughs, salt helps in browning and evening rising. Try to look for Iodine free or “Kosher” Salt for baking purposes. Regular table salt is saltier and has an iodine aftertaste.
Vanilla: Used widely and extensively you should always have some good pure vanilla extract. Vanilla beans are wonderful in delicate flans and puddings etc.. It is relatively expensive. Artificial vanilla essence is very strong and if used should be used carefully. There is also an artificial powder (Vanillin Powder) that is used to add vanilla flavor to your baking. It is useful if you do not want to add the liquid form to your recipe. Artificial vanilla can cause frozen desserts to have an off-taste while pure vanilla will always stay true to the flavor.
Other Extracts: Almond, Orange, Lemon, Butter, Coffee, etc… There is a wide range of extracts that are used in baking. If using artificial essence, it’s good to note that flavors like almond and cherry are sometimes very strong and taste almost chemical-like.
Chocolate: Dark, Sweet, and Semisweet – These are varieties of chocolate made with cocoa solids, cocoa butter, sugar, vanilla and emulsifiers in different ratios. Unsweetened chocolate is pure chocolate without sugar or vanilla. It is also known as baker’s chocolate.
Milk Chocolate is our candy bar chocolate with cocoa solids, milk, sugar, and vanilla. White chocolate is merely cocoa butter, sugar, and vanilla. It does not contain cocoa.
Chocolate chips, come in dark, sweet, semi-sweet, and even white. These are forever used in cookies and muffins and even melted down to make ganache and frostings. Make sure to look for “real chocolate” chips. To properly melt chocolate chips, put them in a bowl in the microwave on medium for 20 seconds at a time( stirring in between) till melted or over a bane Marie till melted while stirring.
Cocoa: Cocoa Powder is pure chocolate without sugar, milk, vanilla, or fat. Dutch Processed Cocoa is cocoa powder that has undergone an alkali treatment. it provides a beautiful darker hue and a subtle but purer taste of chocolate. to measure cocoa powder, use a dry fork to break any lumps side the container itself. Then scoop to measure and level it off.
Dried Nuts and Fruit: Impart great texture and flavor to baking. Walnuts, Almonds, Hazelnuts, Cashewnuts, and the like. Make sure to taste the nuts before using them. Stored nuts sometimes go rancid and must not be used in baking. Sometimes they are already “off” when you open your package. Nuts should be stored in sealed bags in the fridge for 6 months. Toast the nuts to get the maximum flavor out of them ( taking care not to burn). Dried fruits like cranberries, apricots, cherries, and raisins are great for festive cooking. Its good to plump up the dried fruits in boiling water before using them in a recipe. Drain well and place on paper towels before adding.
Spices: Use good quality spices. Freshly ground is best. Store spices in a cool dark place or in the fridge. I store them in tightly lidded glass jars because I use them up quite quickly. Cinnamon, cloves, cardamom, nutmeg, etc are often used in baking.
PROBLEMS WHILE BAKING: Baking Tips
How to keep the top from crusting before the baked goods have fully risen: For yeast doughs and cream puffs, STEAM in the oven can keep the top of the baked goods moist and expanding. One trick is to keep an aluminum pan on the lower rack of the oven with some clean rocks ( from a gardening store). Preheat the oven and pour boiled water over the rocks before you put your bread in to bake. ( Caution: wear Mits and Keep your face away from steam). The steam will keep the dough moist with an even rise.
Some Ovens have a built-in steaming option.
Limit Opening the Oven Door: When you open the oven door you must keep in mind that the temperature DROPS DRAMATICALLY. Even i preheated ovens, if you open the door and take a few seconds to put the pan in the oven, the temperature will fall far below the set temperature. This causes the heating elements to turn up the heat to get the temperature back to the set temperature and can cause burning. Learning how the oven works, will help you understand that opening the oven door can affect the timing and results of your baked goods. It is great if you have someone open the door while you put the pan in and have them close it immediately. Or do it as fast as possible if you are on your own. Even if you need to do a toothpick test, take a good look at the crust before you decide to check on the cake with a toothpick. Avoid all unnecessary opening of the oven door.
Egg whites, are a drying agent. If your cake is too dry, it may be that you have too much egg white in there. Try reducing the egg white in the recipe and replace 1 egg with two egg yolks. On the other hand, if your egg is too soggy, you might need to add an egg white.
Note: When Egg Whites are beaten, they are denatured, and almost partially cooked. They are not as strong structure builders now.. Cakes must have enough “raw” egg to keep the cake from “falling”. That being said, meringues and Angel Food cakes are made entirely of whisked eggs, but these are fatless cakes which is why they work.
Science of THE CAKE: The four primary ingredients in most cakes: Flour Sugar, Fat, and Eggs. There is a science behind the balance of these ingredients. The flour and eggs contain the protein required for setting and holding the cake. However, they can cause drying out of the cake too. Gluten formed in the flour causes water absorption and this removes moisture from the cake. This formation is required but shouldn’t exceed the required limit. Eggs whites are drying agents too. On the other hand, sugar and fat make the cake moist, but they can mess up the structure of the cake. Excess fat, causes the fat to coat the flour and prevent gluten formation and excess sugar prevents proteins from setting and causes a pudding-like texture in cakes.
“Gluten” is the combining of proteins in grains especially wheat, that causes the dough to get its elastic nature or ‘glue’. It helps the dough rise, keep its structure, and gives a chewy texture, depending on the amount of gluten formed.
So for the PERFECT BALANCE: For a successful cake, The Structure Builders ( Eggs and Flour) must be balanced with the Structure Breakers (Sugar and Fat). Perfect Balance of the Builders and Breakers creates a moist and tender cake!
Points to remember for moist cakes: #1: The weight of eggs should be greater than the weight of fat
Remember that fat, includes butter margarine, shortening as well as oil, milk and milk products like buttermilk or cream. So if in a cake recipe, you have 1oz of butter, 2 oz of canola oil, and 1.5 oz of heavy cream, that makes your Total fat = 4.5 oz.
So the weight of eggs, both yolks and eggs should be greater than 4.5 oz.
#2 The weight of the liquid should be greater than the weight of the sugar ( enough to dissolve the sugar as well as help the starch to swell)
Keep in mind that eggs and fat also contain some liquid. Also any liquid flavoring or juices
#3 For High Ratio Cakes (Cakes with a larger ratio of sugar when compared to the other ingredients) : The weight of sugar should be greater than the weight of flour for moist cake ( even if only slightly greater).
Some Points On Cakes – Baking Tips :
Adding flavoring (extracts) to the butter or fat in a recipe help to distribute the flavor best, because fats carry flavor across the baked good.
If a cake has a high sugar content it will brown more on the top. This does not matter for cakes that need to be inverted.
Using whipped cream in cakes makes the cake velvety and moist.
Leavener: Using too much leavener ( baking soda or baking powder), the bubbles formed while baking get too big and collide with each other causing them to float to the surface and pop. Thus the leavening is lost and you end up with a dense cake. Remember that 1 tsp baking powder only contains 1/4 tsp baking soda. Baking soda is the strong stuff that you should take care of while adding.
If the leavener is not evenly distributed, there will be holes in your cake. It is hence important to thoroughly beat in the leavened with your flour and other dry ingredients with a fork or dry whisk. (Sifting the leavened with the flour is not enough evenly distribute the leavener).
Note that in most cases, if you are using SELF RISING FLOUR, the use of leaveners can be omitted altogether, as the SRF already contains evenly distributed leavening agents.
Make your own baking powder by mixing 1 Tbsp Baking Soda with 2 Tbsp Cream of Tartar and 1 ½ Tbsp Corn Starch.
Using Brown Sugar gives you a fudgy texture in cakes.
Methods to slice cake:
#1. Cakes can be sliced using a long serrated knife, moving the cake evenly across the center of the cake in a ‘sawing’ motion.
#2. Dental floss is sometimes used to slice through cakes. Mark the cake on the sides using toothpicks on both sides as a guide. Wrap around the cake with the floss, with the floss resting over the toothpicks. cross the end over each other and pull with both hands on both ends, your cake will be sliced. Slip in a cake board through the slit part to lift up the layer. You can slit 2 or more layers, by marking appropriately with toothpicks.
#3. Cake Leveler: Cake Suppliers have special equipment to easily slice through cakes. it is a wire blade on a stand so it cuts very evenly.
(When slicing cakes, use the best layer for the top of the cake, with icing/filling in between. Also if using any syrup it is best to pour over the cur side as opposed to the crust side)
Links that come in useful:
- Baking can be so much fun, but also CHAOTIC if you are not organized. Here’s a great article on How to Create the Ultimate Home Baking Station.
More to come.








I liked it n thanxxx for acquiring such good knowledge 😘😘😘
Maida is plain flour and can be used wherever Plain flour or APF is called for. the term APF is used more By Americans whereas Plain flour is used more in UK and Australia.